Basics of Suspension On the WRX STI CARS
Ride
Basically, suspensions are employed to deal with hump in road surface, in other words, enhancing ride comfort. When a car rides over a hump, the springs are compressed, store the energy thus provide shock absorption. The energy will be released quickly when the springs bounce back. Dampers are employed to smooth and slow down the bounce motion, this is called "Damping". Without dampers, the car will bounce up and down severely and quickly, this is perceived as uncomfortable. Study found that ride is perceived as comfortable by human when the bouncing frequency is 1 to 1.5 Hz. If it expeeds 2 Hz, most people feel the ride harsh. Therefore ride quality is mostly controlled by the selection of suitable springs and dampers.
Handling
In order to achieve ride comfort, we create suspensions and let the wheels movable with respect to the car body. Inevitably, this create many many problems in handling. When the car is turning quickly into a bend, centrifugal force will roll the car body resulting in a less safety ride. Body roll leads to the weight transfer towards the outside wheels, it also changes the suspensions geometry which changes the camber angles of wheels. Change of camber accompanies with weight transfer result in unwanted understeering or oversteering. If brakes are applied in the bend, castor angles will also be changed, that may further deteriorated understeering / oversteering or even introduces torque steer. (Don't understand ? No problem, you will have a clearer view in the following paragraphs)
Camber - Decisive to understeering and oversteering
This is a very important concept. We must learn this before going on our study.
As shown in below, if a wheel is not perpendicular to the road, then it is cambered. If it leans towards the center of the car, then it is negative cambered. If it leans outwards to the car, it is positive cambered (as shown in the following picture.)
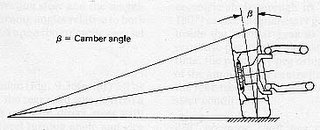 When a wheel has positve camber, due to the elasticity of tyres, the wheel will be reshaped to something like the base of a cone. It will have a tendency to rotate about the peak of the cone, as shown in the picture. Now, you will see the wheel tries to steer away from the center of the car.
When a wheel has positve camber, due to the elasticity of tyres, the wheel will be reshaped to something like the base of a cone. It will have a tendency to rotate about the peak of the cone, as shown in the picture. Now, you will see the wheel tries to steer away from the center of the car.
If both the right and left wheels are positive cambered (that means they lean towards opposite directions), the steering tendency will be cancelled so that the car remains running in straight line. If the car is turning into a corner, body roll puts more weight on the outside wheels than the inside wheels, that means the outside wheel's steering tendency will have more influence to the car. As the positive-cambered outside wheel tries to steer the car to the outside of the corner, the car will be understeered.
On the contrary, if both wheels are negative cambered, the car will oversteer.
A Good Suspension must :
1) Provide independent shock absorption to individual wheels. That means, when one wheel rides over a hump, the shock will not be transferred to other wheels.
2) Has adequate body roll. Excessive body roll leads to too much weight transfer thus influence the steering response. It is not comfortable too. Restrict body roll to minimal may create uncomfortable feeling because of excessive g-force. Moreover, body roll could provide information to the driver, telling him the state of cornering and whether the car has reached its limit. Completely eliminate body roll is not at all good.
3) Has a good geometry such that wheel cambers remain unchanged in all conditions, that is, acceleration, braking, cornering, load and bumps.
Body roll suppression usually conflict with ride comfort, because the former requires stiffer spring and dampers while the latter vice versa. Nevertheless, clever suspension geometry may improve body roll without altering the ride. Here in below we are going to discuss the most popular kinds of suspension geometry.
Comments